-
December 1, 2025
Lipoma Lumps: What Is It, Causes, Symptoms, Types, Treatment
Lipoma lumps are among the most common noncancerous (benign) soft-tissue growths found in adults. These fatty lumps develop just under the skin and can appear anywhere on the body. While a lipoma may look or feel concerning, most lipoma lumps are harmless, slow-growing, and painless.
Understanding what lipomas are, what causes them, how they feel, and when you should see a doctor can help reduce worry and support better decision-making about your health.
What Are Lipoma Lumps?
A lipoma is a benign fatty tumor made of soft, rubbery fat cells trapped under the skin. Although the word “tumor” sounds alarming, lipomas are not cancerous and rarely become dangerous.
Lipomas can occur in people of all ages but are most common in adults between 40 and 60 years old.
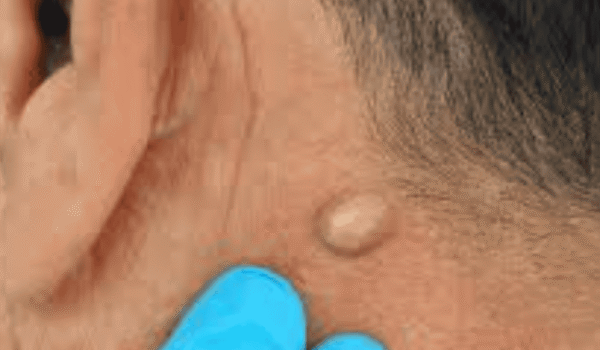
What Do Lipoma Lumps Feel Like?
Lipoma lumps typically have very distinct features. They often feel:
-
Soft or rubbery
-
Painless
-
Moveable under the skin (they glide when pressed)
-
Slow-growing
-
Round or oval in shape
Some lipomas may grow larger over time, but they usually remain harmless.
Symptoms that may accompany a lipoma include:
-
Visible bulge under the skin
-
Mild discomfort if the lipoma presses on nerves
-
Tenderness (rare)
Lipomas most commonly appear on:
-
Neck
-
Shoulders
-
Back
-
Arms
-
Thighs
-
Abdomen
What Does a Cancerous Lump Feel Like Compared to a Lipoma?
Cancerous lumps (liposarcomas) are rare but different from lipomas.
A cancerous lump may be:
-
Harder or firmer
-
Larger and rapidly growing
-
Fixed in place (not movable)
-
Painful or tender
-
Irregular in shape
If a lump grows quickly, becomes painful, or feels significantly different from a typical lipoma, you should seek medical evaluation promptly.
Causes of Lipoma Lumps
The exact cause of lipomas is not fully understood, but common factors include:
1. Genetics
Lipomas often run in families. Conditions like familial multiple lipomatosis cause multiple lipomas.
2. Minor Injuries
Some lipomas develop after trauma or blunt injury, although this connection is not always clear.
3. Medical Conditions
Certain conditions increase the likelihood of developing lipomas, such as:
-
Dercum’s disease
-
Madelung’s disease
-
Adiposis dolorosa
4. Age & Lifestyle Factors
People between 40–60 years old are more likely to develop lipoma lumps.
Lipomas are not caused by obesity, even though they consist of fat tissue.
Are Lipoma Lumps Normal?
Yes—lipomas are very common. Most people who develop a lipoma have no underlying health problem. Many lipomas remain small and never cause complications.
Do Lipomas Mean Cancer?
No. Lipomas are noncancerous. They do not turn into cancer.
However, a lump that grows quickly, becomes painful, or feels very firm should be checked to rule out a more serious condition.
Can Lipomas Be Caused by Infection?
No. Lipomas are not caused by infection and do not spread through the body.
However, other lumps—such as abscesses—can resemble lipomas, which is why medical evaluation is sometimes needed.
How Are Lipoma Lumps Diagnosed?
If you visit a healthcare provider for a lipoma lump, they may perform:
1. Physical Examination
Your doctor will check:
-
Size and shape
-
Texture
-
Mobility under the skin
-
Whether there is pain or tenderness
2. Imaging Tests (if needed)
These are used when the lump is large or unusual:
-
Ultrasound
-
MRI
-
CT scan
3. Biopsy
Rarely required—only done if the lump has atypical features or rapid growth.
Do Lipomas Go Away on Their Own?
No. Lipomas usually do not shrink or disappear naturally.
However, many lipomas stay small and don’t cause symptoms, so no treatment is required.
Treatment Options for Lipoma Lumps
Lipoma treatment depends on size, symptoms, and personal preference.
1. Observation
If the lipoma is small and painless, no treatment is necessary.
2. Surgical Removal
A small incision is made to remove the fatty lump completely. This is the most common and permanent treatment.
3. Liposuction
Used for large or soft lipomas; removes fatty tissue using suction.
4. Steroid Injections
May shrink the lipoma but won’t remove it entirely.
Lipomas do not respond to antibiotics or medication, as they are not infections.
How to Maintain Healthy Skin & Prevent Lipoma Complications
While lipomas cannot always be prevented, you can maintain overall skin and soft-tissue health by:
-
Monitoring new lumps or changes
-
Maintaining a healthy weight
-
Staying physically active
-
Eating anti-inflammatory foods
-
Avoiding repeated skin trauma
-
Getting regular medical check-ups
When Should You See a Doctor for a Lipoma Lump?
Seek medical evaluation if you notice:
-
Rapidly growing lumps
-
Painful or tender lumps
-
Lumps larger than 5 cm
-
Lumps that feel firm or fixed
-
Lumps causing movement restriction
-
Changes in color or skin appearance
Early diagnosis helps ensure the lump is benign and manageable.
Common FAQs About Lipoma Lumps
Can Lipomas Develop in Multiple Locations?
Yes. Some people develop several lipomas across the body, especially if they have a genetic predisposition.
Can Lipomas Become Cancerous?
No. Lipomas themselves do not turn into cancer.
Are Lipomas Dangerous?
Most are harmless. They only become concerning if they grow quickly or press on nerves.
Can Diet Cure a Lipoma?
No diet can remove a lipoma, but maintaining a balanced diet supports overall skin health.
Final Thoughts
Lipoma lumps are common, harmless fatty growths that typically require no treatment unless they become painful, large, or bothersome. Understanding the features, causes, symptoms, and treatment options for lipomas can help you make confident and informed decisions about your health. If you ever feel uncertain about a lump, always consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation.
drtomarswellness.com
Dr. Jitender Tomar™ – TEDx Speaker, Founder of Dr. Tomars Wellness™, Doctor2Brand™, and Visionary of the Chemical-Free India™ Movement.
Related Posts
Comments are closed.













2 Comments