-
November 28, 2025
Cavity Made Easy: Why They Happen, Symptoms, Tests, and How to Fix Them
A cavity—also known as tooth decay or dental caries—occurs when the hard surface of a tooth becomes permanently damaged due to bacterial activity. Cavities are one of the most common dental problems worldwide, affecting children, adults and older individuals. Understanding cavity causes, cavity symptoms, cavity diagnosis and cavity treatment is essential for maintaining long-term oral health.
What Is a Cavity?
A cavity is a small hole or area of decay in the tooth enamel. It begins when plaque bacteria react with sugars from food to produce acids that erode the enamel layer. If left untreated, the cavity grows deeper, eventually reaching the dentin and pulp, leading to pain, infection and even tooth loss.
Because cavities are extremely common and preventable, many people search online for:
-
What causes cavities
-
Early signs of a cavity
-
How to treat a cavity
-
How to prevent cavities
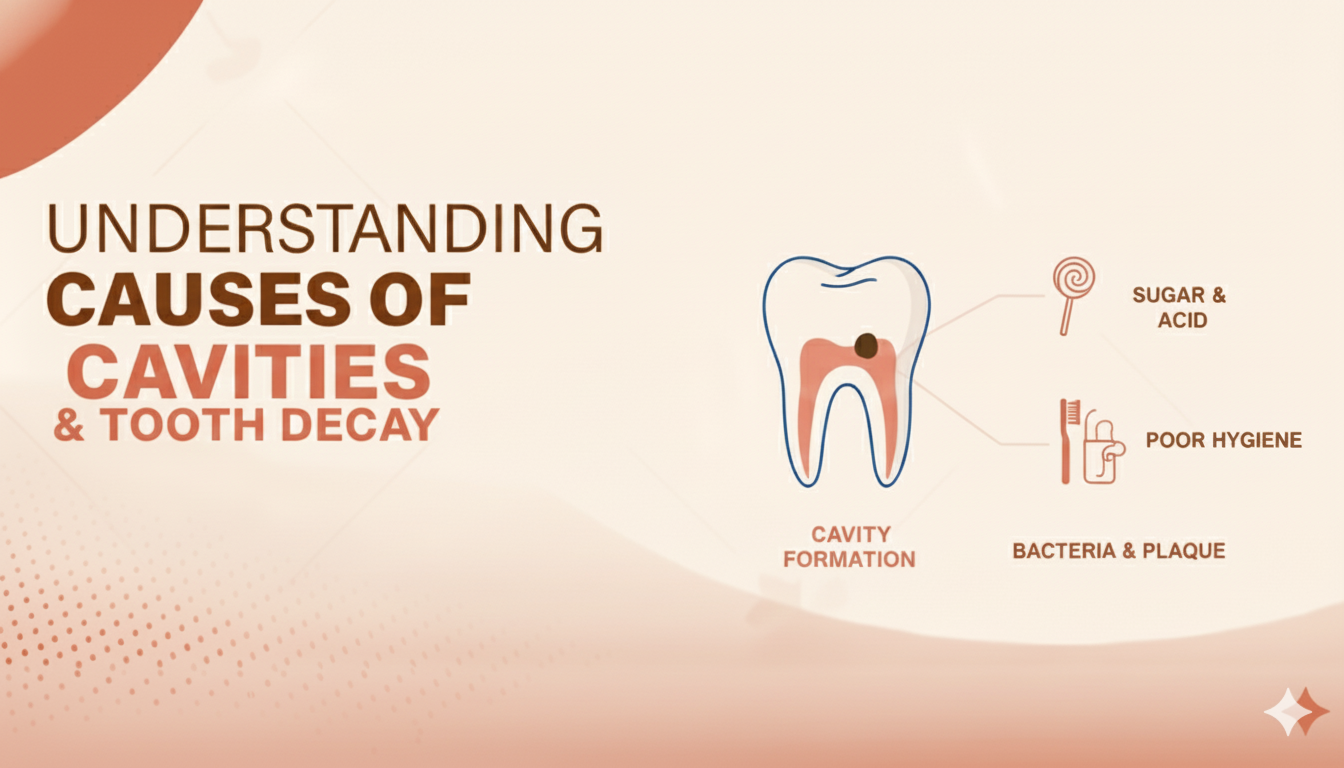
Cavity Causes
A cavity does not appear suddenly. It develops gradually through a combination of lifestyle, diet and oral hygiene factors.
Main Causes of a Cavity
-
Poor Oral Hygiene
Not brushing or flossing properly allows plaque to build up and attack tooth enamel. -
Sugary and Acidic Foods
Candy, soda, fruit juices, and sticky snacks increase cavity risk. -
Bacteria Buildup
Streptococcus mutans, the main cavity-causing bacteria, thrives on leftover food. -
Dry Mouth
Reduced saliva allows acids to stay longer on teeth. -
Acid Reflux
Stomach acids can erode enamel over time. -
Genetic Factors
Some people naturally have weaker enamel, making cavity formation easier.
Understanding the cause is key to preventing cavity progression.
Cavity Symptoms
Early cavity symptoms may be mild and easy to miss. As the cavity deepens, symptoms become more noticeable.
Early Cavity Symptoms
-
Sensitivity to hot, cold or sweet foods
-
Mild pain when biting
-
White or brown spots on teeth
Moderate Cavity Symptoms
-
Visible hole or pit in the tooth
-
Persistent toothache
-
Sharp pain while chewing
-
Discoloration that becomes darker
Severe Cavity Symptoms
-
Intense pain
-
Swelling of gums
-
Pus formation
-
Bad breath
-
Difficulty eating
If severe cavity symptoms appear, immediate dental treatment is necessary.
Cavity Diagnosis
Dentists diagnose a cavity using a combination of visual examination and imaging tests.
Common Cavity Diagnosis Methods
-
Visual Inspection
Dentist checks for holes, discoloration or surface softening. -
Dental Probe
Used to check for enamel weakness or sticky areas. -
X-rays
Detect hidden cavities between teeth or under old fillings. -
Laser Cavity Detection
Advanced tools that identify early stages of tooth decay.
Accurate cavity diagnosis ensures early and effective treatment.
Cavity Treatment
Cavity treatment depends on how advanced the decay is.
1. Fluoride Treatment (Early Cavity)
Strengthens enamel and reverses early decay.
2. Dental Fillings (Moderate Cavity)
Dentist removes decay and fills the cavity using:
-
Composite resin
-
Amalgam
-
Glass ionomer
3. Dental Crowns (Large Cavity)
Used when a large portion of the tooth is damaged.
4. Root Canal Treatment (Deep Cavity)
Required when decay reaches the pulp and causes an infection.
5. Tooth Extraction (Severe Cavity)
Only necessary when the tooth cannot be saved.
Timely cavity treatment prevents costly and painful dental complications.
How to Prevent a Cavity
Prevention is the best way to avoid cavity formation.
Cavity Prevention Tips
-
Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
-
Floss daily to remove plaque between teeth
-
Limit sugary and acidic foods
-
Drink plenty of water
-
Use mouthwash that kills cavity-causing bacteria
-
Visit the dentist every 6 months
-
Avoid frequent snacking
Good oral hygiene practices greatly reduce the chances of developing a cavity.
When to See a Dentist
You should see a dentist if you notice:
-
Sudden tooth sensitivity
-
Pain while eating
-
Visible dark spots on teeth
-
Persistent bad breath
-
Any early cavity symptoms
Delaying treatment can cause a simple cavity to turn into a severe dental infection.
Conclusion
A cavity is a preventable dental problem, but when ignored, it can lead to pain, infection and tooth loss. Understanding cavity causes, cavity symptoms, cavity diagnosis and cavity treatment empowers individuals to take control of their oral health. With proper care, regular dental checkups and good hygiene habits, cavities can be avoided and treated effectively.








Leave a comment