What Is a Hernia?
A hernia occurs when an internal organ or tissue pushes through a weak area in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. It often appears as a visible bulge or lump, especially when coughing, bending, or lifting heavy objects.
Hernias commonly occur in the abdomen but can also develop in the groin, upper thigh, or chest area (diaphragm).
Common Symptoms of a Hernia
Symptoms vary depending on the type and severity of the hernia, but common signs include:
- A visible bulge in the affected area
- Pain or discomfort when coughing, lifting, or bending
- A feeling of pressure or heaviness in the abdomen or groin
- Burning or aching sensation at the site of the bulge
- Difficulty swallowing (hiatal hernia)
- Nausea or vomiting in severe cases
Seek immediate medical attention if the bulge becomes painful, hard, discolored, or cannot be pushed back in. These may be signs of a strangulated hernia, which is a medical emergency.
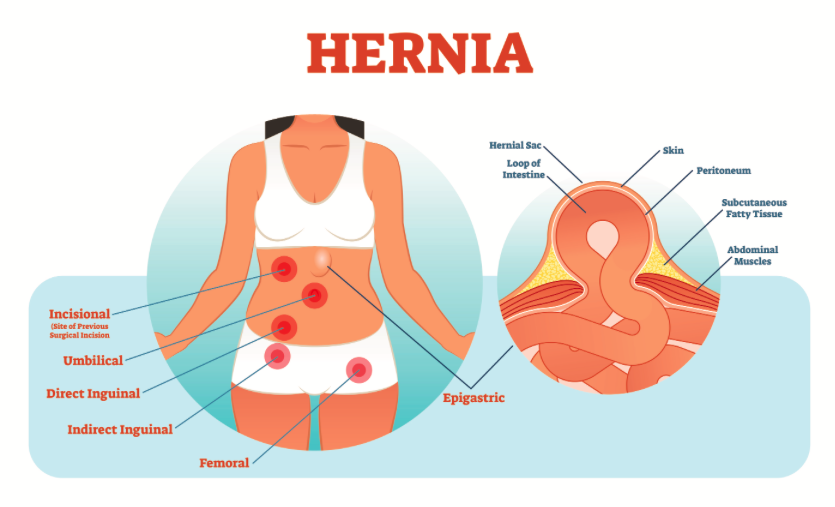
Types of Hernias
Inguinal Hernia
The most common type of hernia. It occurs when tissue pushes through a weak spot in the groin area and is more common in men.
Femoral Hernia
Less common and more frequently seen in women. It appears as a lump near the upper thigh.
Umbilical Hernia
Occurs near the belly button. It is common in infants but can also develop in adults.
Hiatal Hernia
Happens when part of the stomach moves upward through the diaphragm into the chest cavity. It is often associated with acid reflux.
Incisional Hernia
Develops at the site of a previous abdominal surgery due to weakened tissue.
Epigastric Hernia
Occurs between the belly button and the chest, usually caused by weak abdominal muscles.
What Causes a Hernia?
Hernias develop due to a combination of muscle weakness and physical strain.
Factors That Weaken Muscles
- Congenital weakness (present at birth)
- Aging
- Previous surgery
- Injury
- Chronic coughing
Strain Factors
- Heavy lifting
- Chronic constipation
- Persistent coughing or sneezing
- Pregnancy
- Sudden weight gain
- Intense physical activity
Risk Factors
You may have a higher risk of developing a hernia if you:
- Are overweight or obese
- Smoke (weakens connective tissues)
- Have a family history of hernia
- Perform physically demanding work
- Have chronic cough or constipation
How Is a Hernia Diagnosed?
Doctors usually diagnose a hernia through:
- Physical examination
- Imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI if needed
Treatment Options for Hernia
Hernias do not heal on their own. Treatment depends on the size, symptoms, and type of hernia.
Watchful Waiting
For small and painless hernias, doctors may recommend monitoring the condition without immediate surgery.
Hernia Surgery
Surgery is the most effective treatment. Common surgical options include:
- Open Hernia Repair: The surgeon makes an incision and reinforces the weak area, often using surgical mesh.
- Laparoscopic (Minimally Invasive) Repair: Performed using small incisions and a camera, offering faster recovery.
Lifestyle Management for Hiatal Hernia
- Dietary changes
- Weight loss
- Medications to reduce acid reflux
Prevention Tips
While not all hernias can be prevented, you can reduce your risk by:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding heavy lifting or using proper lifting techniques
- Treating chronic cough or constipation
- Strengthening abdominal muscles through exercise
- Avoiding smoking
When to See a Doctor
Consult a doctor if you experience:
- A noticeable bulge
- Pain or discomfort that worsens
- Persistent heartburn or acid reflux
Seek emergency care immediately if you have severe pain, nausea, vomiting, or a hard and immobile bulge. These symptoms may indicate a strangulated hernia.
Final Thoughts
Hernias are common and treatable. Early diagnosis and proper treatment can prevent complications and help you return to normal activities quickly. If you notice symptoms or have concerns, consult a qualified healthcare professional.
Medical Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for medical concerns.